z/HPF I/O for Dumps
Abstract
In APAR VM66431 IBM changed SNAPDUMP, abend dumps, and PSW restart dumps to use z/HPF I/O if the hardware supports it. This change improves the speed of dump I/O and so it reduces the amount of time needed to produce a dump. In our measurements the time needed to produce a dump was cut by about half. Customer results will vary.
Introduction
In 2008 on the z10 family of processors IBM introduced High Performance FICON, also known as z/HPF. z/HPF I/O is less complex than traditional FICON I/O and so it is more efficient. In this article we described the effect of z/HPF on CMS application I/O. In another article we described the effect of z/HPF on paging I/O.
Internal experiments with using z/HPF I/O for dump I/O led to the PTF discussed in this article. Below we present the results of the internal experiments. IBM never did formally measure the shipped PTF. Because the shipped PTF contains the same code as the last experimental driver, and because dump is such a simple operation, we publish here the experimental results.
Method
On a z14 running z/VM 7.2 we brought up a workload in a 256 GB partition. This partition size gave us enough to dump for a suitable experiment. Then we issued SNAPDUMP. All dumps included the frame table and did not include PGMBKs. Then we issued DUMPLOAD. Each of our DUMPLOAD output files ended up being about 550,000 4 KB records in size.
The dump file contains metadata that tells us the partition storage size, what kind of dump it was, the number of I/Os done, the elapsed time, and of that elapsed time, how much of it was I/O wait time. An exec mined the metadata out of the dump file and produced a small report for us.
We did the experiment first with a z/VM CP that used classic I/O and then with a z/VM CP that used z/HPF I/O.
Results and Discussion
Table 1 gives the result of the experiment.
| Table 1. Effect of z/HPF on SNAPDUMP. | ||||
| Run name | RRR0 | RRR6 | Delta | Pct |
| I/O type | classic | z/HPF | ... | ... |
| Total elapsed time, sec | 26.2 | 14.3 | -11.9 | -45.4 |
| Size of dump, 4 KB records | 550442 | 550398 | -44.0 | 0.0 |
| Number of I/Os done | 4830 | 5012 | 182.0 | 3.8 |
| Records per I/O | 114.0 | 109.8 | -4.2 | -3.7 |
| I/O wait time, sec | 22.2 | 10.3 | -11.9 | -53.6 |
| Time per I/O, msec | 4.59 | 2.06 | -2.5 | -55.1 |
| Time per record, usec | 40.3 | 18.8 | -21.5 | -53.3 |
| Notes: z14, 3906-M05, dedicated partition. 2412-951 with four FICON Express8S LX chpids. z/VM 7.2 internal driver, without or with z/HPF dump enhancement. | ||||
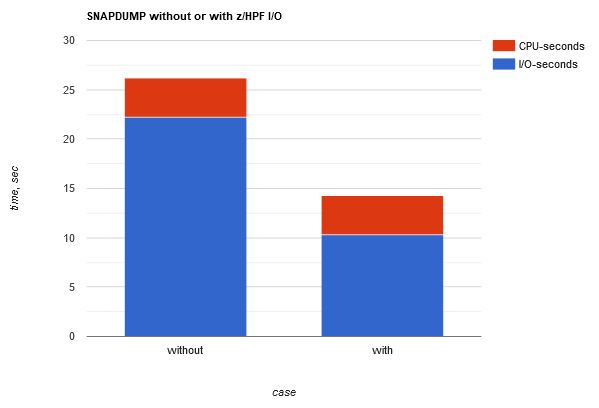
Figure 1 illustrates the differences in I/O wait time and total elapsed time.
| Figure 1. SNAPDUMP time, without or with z/HPF. |
|
| Notes: z14, 3906-M05, dedicated partition. 2412-951 with four FICON Express8S LX chpids. z/VM 7.2 internal driver, without or with z/HPF dump enhancement. |
Summary
The z/HPF enhancement reduced our dump I/O wait time by about 53%. This in turn decreased our dump elapsed time by about 45%.